Modular construction
Volumetric modular construction (VMC) is a new construction approach which has recently attracted a lot of interest and investment worldwide. In VMC, 3D volumetric modules are already designed and prefabricated offsite (in a remote factory) and then they are transported and assembled onsite. VMC is preferred to traditional onsite construction methods in terms of construction time, workplace safety, material usage, onsite workload, environmental impacts, sustainability benefits and quality control. Based on a recent project, VMC can decrease construction time and cost by 50% and 20%, respectively.
As a new, fast, and cost-effective technique, VMC is deemed to revolutionize the construction industry and provide a robust and reliable solution to upcoming housing crisis. The full advantage of modular construction can be exploited in structures with many repetitive architectural plans such as mid- to high-rise hotels, hospitals, schools, and classrooms.
Nowadays, the applicability and feasibility of modular construction have been properly demonstrated in low-rise structures by implementing a lot of projects worldwide, while application of modular construction in high-rise structures is limited so that less than 1% of modular structures are high-rise and most of mid- to high-rise modular structures are built in none-or low-seismic zones.
There are some significant challenges in developing high-rise modular buildings such as lack of standard and well-established design guidelines, lack of strong and robust connection techniques, lack of accurate numerical simulation methods and lack of understanding of global seismic behavior and structural robustness of high-rise modular structures. Due to abovementioned challenges, academia and industry are not confident enough to develop high-rise modular structures widely.
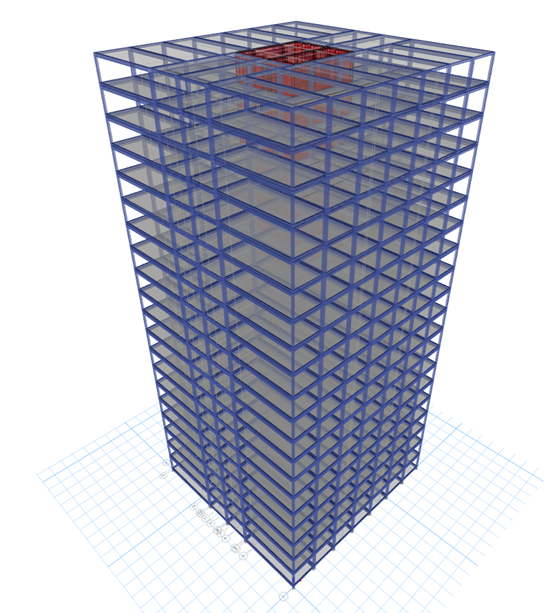
Therefore, understanding the seismic behavior of high-rise modular buildings considering its modular characteristics (volumetric modules, module-to-module connections, module-to-core connections) in high-seismic zones such as Vancouver is crucial.


Modular Construction Projects
There are two research projects related to modular structures in Smart Structures Lab:
1) Development of High-Performance Modular Steel Systems for Seismic Applications. 2) Design Guideline for High-Rise Volumetric Modular Buildings in Canada.
The first project is a collaborative 2-year project among The University of British Columbia and four industry partners including: WSP, Stantec, Stack Modular and Bird Construction.

The objective of this project is to investigate the seismic performance of high-rise modular structures that can be constructed in high-seismic areas such as Vancouver. The outcome of the research will be the next-generation modular structural systems that can be implemented by the industry partners to build high-performance, and resilient high-rise buildings. This will result in fast, economical, and more resilient infrastructures to be built in Canada and around the world.
The second project is collaborative 4-year project between UBC and NRC. The objectives of this research are to investigate the most significant research gaps related to high-rise modular structures including: I) lack of standard and well-established design guidelines; II) lack of strong and robust connection techniques; III) lack of accurate numerical simulation methods and, IV) lack of understanding of global seismic behavior and structural robustness of high-rise modular structures. The outcomes of this research consist of developing design guideline, robust connection techniques and accurate numerical simulation methods for high-rise modular structures.
High-rise modular prototype in these projects consist of ductile concrete core (as the SFRS) and volumetric steel modules as the gravity system. The typical volumetric steel modules and the numerical model of the high-rise modular prototype for these projects are shown in the following figures.